An Emergency Action Plan plays a crucial role within broader employee health and safety programs and outlines the steps for employees to follow during emergencies. The answers to how an emergency action plan benefits your workplace are many, but the most important is ensuring employee safety and confidence in the organization. It also helps minimize property damage and financial loss and facilitates better coordination with external emergency services.
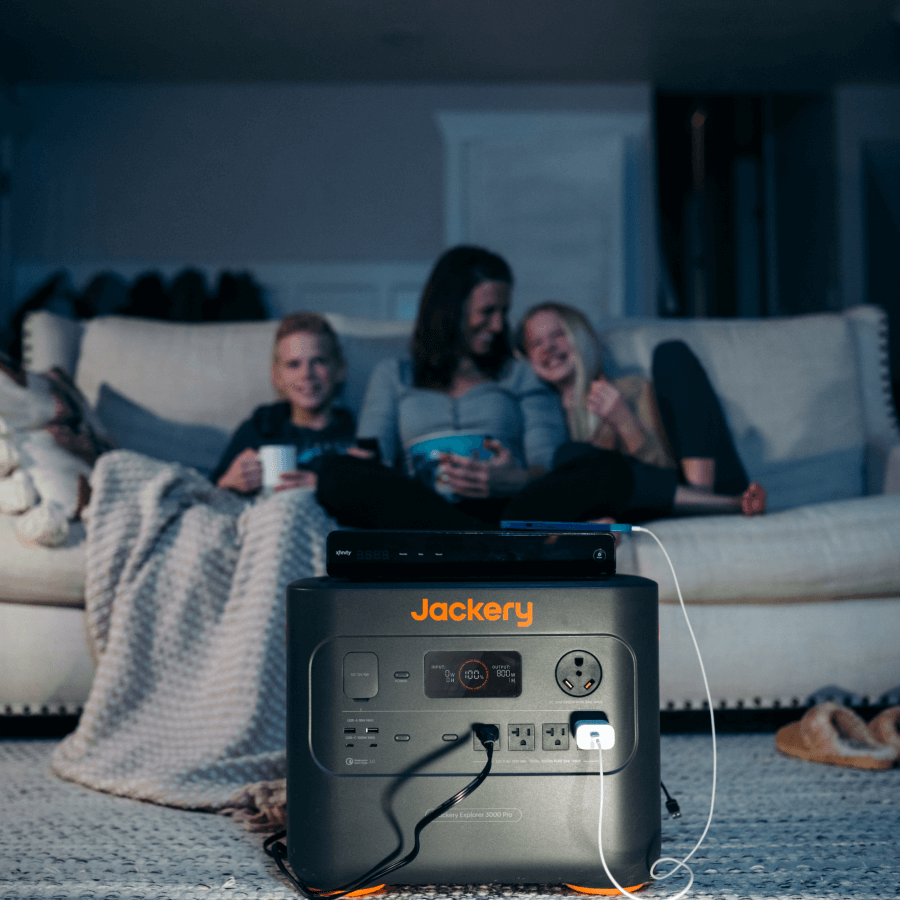
Irrespective of preparedness, emergencies are often followed up with hours of power outages and blackouts, so having a reliable solar generator comes in handy. Jackery Solar Generators are one of the best in the market, and they can power your appliances for hours without any issues.
Key Takeaways
- EAP is necessary to keep employees and employers safe during emergencies like fire, natural disasters, workplace violence, etc.
- EAP has several benefits, including ensuring employee safety, reducing response time, minimizing property damage, and reducing financial loss.
- Some essential elements of workplace EAP include emergency contact information, exit routes, alarm systems, communication protocols, and personal protective equipment.
- To make an EAP for at-risk workers, conducting a thorough risk assessment, documenting worksites and facilities, keeping employees involved, and assessing available resources are essential.
What Is An EAP in The Workplace
An EAP, or Emergency Action Plan, is a written document prepared per OSHA standards [29 CFR 1910.38(a)] that details the workplace’s response to an emergency. Its underlying purpose involves an employee and employer adopting a proactive approach to staying safe during workplace emergencies.
Some common workplace emergencies are fire, tornados, earthquakes, and landslides. The nature of emergencies dictates the course of action outlined in the EAP document. For example, in the event of a fire, individuals must be evacuated from the building, while in an earthquake, individuals must stay away from debris.
- Fire: Fire is a serious workplace safety threat that can result in fatalities, injuries, and extensive property damage. It can be caused by electrical faults, flammable materials, or human error.
- Natural Disasters: An EAP includes natural disasters such as tornadoes, earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes.
- Workplace Violence: It’s an act or threat of violence, intimidation, harassment, or any disruptive behavior in a workplace.
- Medical Emergencies: A medical emergency is an injury, illness, symptom, or any similar condition that requires immediate care to prevent severe harm. Some examples include breathing problems, chest pain, bleeding, etc.
- Material Incidents: Material incidents are the most common workplace emergencies. It encompasses gas leaks, chemical spills, machinery malfunctions, and electrical hazards.
Other than these, active shooter situations, bomb threats, workplace violence, and similar must be included in the EAP document. In these cases, you must set the procedures in accordance with the proximity of the event.
Irrespective of the emergencies, workplaces must develop curated plans and provide employee training accordingly to reduce injuries and structural damage. A poorly prepared plan potentially results in a disorganized emergency or evacuation response, resulting in injury, confusion, and property damage.
How Does An EAP Benefit Your Workplace
Implementing an EAP in your workplace has several benefits, which are detailed as follows:
Ensure Employee Safety: Having a clear EAP helps employees take appropriate actions during emergencies, such as acting calmly, knowing how to leave the building, and keeping clients and customers safe. In this way, emergencies won’t inflict any injuries on the employees.
Reduce Response Time: When employees have an EAP and know what to do, they can act promptly and effectively. This can potentially save many lives and minimize the impact of emergencies.
Minimize Property Damage: A well-designed EAP includes the procedures for safely handling materials and equipment during emergencies and significantly reducing property damage. For instance, if you understand the right way to handle hazardous waste or shut down machinery, you can prevent further damage during emergencies like spills or fires. Besides, their regular maintenance also minimizes the risk of such emergencies in the future.
Foster Employee Confidence: Knowing there’s a plan to deal with the dangers of workplace emergencies boosts employee morale and confidence and contributes to a positive work environment. They feel protected by the employer, which translates into a productivity boost and a stronger sense of community within the workplace.
Facilitate Communication: With any disaster hitting a workplace, a negative perception develops regarding the incident. Having a curated EAP lets you keep your clients and stakeholders informed about the scenario, irrespective of the impact the disaster has caused on workplace practices.
Reduce Financial Loss: Emergencies, irrespective of their type (fire, natural disaster, chemical spills, or others), can cause severe financial consequences for a business. However, a properly implemented EAP lessens the impact by minimizing property damage, identifying alternative facilities or backup supplies to continue production, and making better decisions regarding insurance coverage.
In this way, the business has a financial shield in place, which protects it against devastating costs associated with emergencies and ensures a fast recovery.
Better Coordination With External Emergency Services: Often, businesses establish communication protocols and liaison points with external emergency services through workplace emergency evacuation plans. You can ask for quick help in emergencies to minimize damage and injury.
Compliance With Legal and Insurance Requirements: Businesses in many regions or states have legal requirements regarding emergency preparedness in the workplace. Having an EAP lets businesses comply with these regulations and demonstrate commitment towards safety, which further benefits them in terms of lower insurance premiums and better terms.
How to Create An EAP for Workplace
Creating an EAP requires a customized approach tailored to the specific needs of each business. This includes detailed workplace safety procedures that address potential risks and challenges unique to the employees and the business. Having said this, cover the following components in an EAP:
- Emergency Contact Information: Your EAP must list the important contacts, including medical facilities, fire departments, and local emergency services.
- Exit Routes: The plan must mark the evacuation routes and instructions for employees during evacuations.
- Alarm Systems: Clear mention of the details regarding the ways employees will be alerted during emergencies, including sirens, alarms, etc.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assign each employee respective roles and responsibilities, such as alerting others, evacuating, performing first aid, or contacting emergency services.
- Communication Protocols: EAP must establish communication protocols for employees to request assistance and report emergencies or other critical situations.
- Training Employees: The ways to train employees during emergencies should be mentioned, and sessions should be carried out accordingly.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Lastly, the EAP must list where employees can access the PPEs and how to use them during emergencies.
Now you have a clear view of what to include in an emergency action plan, it’s time to create it. Here are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Collaborative Approach
Start by involving employees at all levels when developing an EAP. This way, you invite diverse perspectives and increase ownership of the plan, resulting in greater engagement.
Step 2: Identifying the Hazards
The most crucial step in preparing an emergency action plan is to identify the hazards expected at your workplace. For example, spilling chemicals at any chemical plant is considered a major risk. Creating a plan highlighting the potential hazards identified during routine inspections, such as weakened storage containers, faulty equipment, etc., and developing solutions helps employees understand the dangers and stay safe.
Step 3: Prepare a Written Document
Based on your research and considering the OSHA regulations, create a detailed and accessible written document that serves as an EAP template. Share it with your employees and ensure it’s easily updatable in the future.
Step 4: Review and Update
Review and update the document periodically to account for the changes in regulations, personnel, and overall workplace. Also, make sure to inform employees about the updates.

As you have an EAP, it’s time to prepare and train for it to follow during emergencies. Here’s what to do:
Make the Document Accessible: Keep the written document at a location where it’s easily accessible for the employees, or you can send a soft copy through email. They must familiarize themselves with it at their convenience. Review and share the EAP in meetings periodically.
Employee Training: Train the employees in roles corresponding to the EAP procedures. When feasible, hold training exercises with the EAP for employees to familiarize themselves with the situation and the execution procedure. In this way, they will become familiar with the roles and responsibilities for which they are accountable during emergencies.
Regular Updates: Circumstances might change over time; therefore, updating the EAP regularly is crucial to accommodate them and ensure maximum safety. Also, ensure to include the changes to the floor plan.
Again, these are general guidelines for preparing for EAP, and preparation must be based on EAP details and the necessities of respective businesses.
Tips for Making An EAP for At-Risk Workers
Depending on your business and other relevant aspects, there are multiple ways to develop a curated emergency action plan. Here are a few tips to help you in this respect:
Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment
The primary purpose of an EAP is to analyze the possible risks and create a plan to deal with them effectively. Therefore, a risk assessment is vital in drafting an emergency action plan. You thoroughly inspect your workplace to understand the most vulnerable areas and potential risks.
Other than that, prepare a backup plan for the unlikely risks that might not be suitable for your business or location so that you can stay extra safe. Then, create an action plan to address each risk effectively and minimize the potential damage.
Document Your Facilities and Worksites
Documenting your workplace's structural layout and floor plan is crucial when making an EAP. It should clearly point out the entrance and exit routes, location of emergency equipment, security systems, and utility controls. This way, employees and emergency personnel can understand where to go during emergencies and how to access controls, such as protective gear.
Access Available Resources
When creating an EAP, consider the available internal and external resources to ensure a prompt and effective emergency response. External resources include public services like fire departments, law enforcement, and fire departments, while internal resources encompass all the on-site tools such as alarm systems, fire extinguishers, and individuals present.
Ensure that you carefully jot down the names and contact information of emergency services and individuals so there isn’t any confusion during an emergency.
Keep Employees Involved
Employees are responsible for executing the evacuation plan and ensuring everyone at the spot is safe. Therefore, creating a rough draft and gathering employee feedback is essential. Different perspectives help you gather valuable insights that you might have missed earlier.
Tips for Implementing An EAP in Your Workplace
Implementing the prepared EAP requires support from both employers and employees, and the result is everyone is clear on their respective roles. Follow the tips to implement the EAP in your workplace:
Prepare Resources and Support
Successful implementation of the emergency action plan depends on the availability and utilization of adequate resources and support. To that end, store the EAP in a centralized online location where employees can easily access the required information. Then, designate an individual to promote the program within the team and ask them for feedback, if any.
Regular Drills and Training
For a proper EAP implementation, employers need to train their employees so that they understand their roles and responsibilities. Although employees have many individual duties, employers must ascertain the most important ones and train the employees regularly, with any new regulations or action plans added to the document.
Identify and train the employees to carry out their respective evacuation and post-evacuation duties and conduct training exercises periodically to ensure they won’t make mistakes in real-life situations.
Appoint Leaders
The procedures and regulations within your emergency action plan require a leader who can oversee and coordinate your business emergency responses. These leaders represent members at varying levels, whether managers or employees. You can delegate them specific responsibilities such as evacuating or turning off the equipment or give them special authority to implement the emergency procedures. This way, employees know who to turn to when an emergency occurs.
Establish a Proper Communication Protocol
Businesses periodically undergo changes in personnel, policies, and regulations, so establishing a communication protocol is crucial to ensure everyone is well aware of these changes. You can delegate personnel for that and ask them to encourage suggestions and participation from everyone involved.
Jackery Solar Generators for Emergencies
Many emergencies, such as natural disasters, power outages, and others, damage property. Manufacturing ceases, production ceases, and consumers are unable to receive services. Besides, employees can’t operate their equipment without an emergency electricity source, while higher administration can’t access digital resources. Here, a reliable backup power solution gets your operations back on track.
Jackery is an industry-leading manufacturer of solar panels, portable power stations, and solar generators. Since its inception, it has sold over four million units and earned several accolades for its exceptional work in this industry. Jackery Solar Generators combine Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels and Jackery Portable Power Stations to collect, convert, and transmit electricity to power domestic and commercial appliances during a power outage.
These are valuable companions during emergencies. They pack enough power to run most of your appliances and let you get operations back on track until the power comes back on.
Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro
Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro has an excellent capacity and power output to cover most of your electrical needs. It can charge 99% of your appliances, including computers, laptops, routers, lights, and others, for an extended time, so you can continue communicating with clients and customers and processing orders despite emergencies.
Appliances Running Time
- Light (60W): 42.8H
- TV (300W): 8.5H
- Fan (60W): 42.8H
- Computer (100W): 25.7H
- Refrigerator (1000W): 2.5H

Customer Review: “Sent right away. Works great so far with home charge and solar charge. Will be hooking it up to my pop-up camper next week. Great size, quiet and good app so far.” - James Matthews.
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is suitable for businesses that need to power a decent set of appliances like laptops, computers, TVs, lights, and similar during hours of power outage. Once solar-charged, it can power up to eight appliances simultaneously. The best part is that its ergonomic design and wheels make it easy to carry around on whichever office floor needs it.
Appliances Running Time
- Light (60W): 28.9H
- TV (300W): 5.7H
- Fan (60W): 28.9H
- Computer (100W): 17.3H
- Refrigerator (1000W): 1.7H

Customer Review: “Best investment for our business we do craft shows. We use the Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus with 2 SolarSaga 200W panels to power our XTool F1 portable laser air purifier laptop and lights on our canopy, and if the power goes out, I can power my CPAP machine with no need to pay the vendor for electricity.”- Kevin J. Craig
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus Kit (4kWh)
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus Kit (4kWh) is a robust charging solution designed for various emergencies, power outages, and blackouts or even reducing dependence on electric grids. It can run 99% of the appliances, including heavy-duty appliances like refrigerators, air conditioners, etc., for hours, so you don’t have to worry about disruption in operations due to emergencies.
Appliances Running Time
- Light (60W): 57.8H
- TV (300W): 11.5H
- Fan (60W): 57.8H
- Computer (100W): 34.7H
- Refrigerator (1000W): 3.4H

Customer Review: “This is absolutely a great addition to the 2000 Plus. I mainly have this for power outages, but I will use this on the occasional camping trip. I will probably buy an additional pack to make my supply 6k.”- Mark Watkins.
Workplace Emergency Action Plan Example
An emergency action plan must comply with OSHA’s standard for Emergency Action Plans, 29 CFR 1910.38, with added information to your site-specific plan. Here’s an example of an EAP which you can follow:
Date Created:
Date Reviewed:
- Company Policy
Include the company policy in compliance with OSHA EAP Standard 29 CFR 1910.38 and the primary purpose of designing the plan.
- Assignment of Responsibility
Name the individual(s) responsible for managing the emergency action plan. The person will manage the resources, communicate with emergency services, and train the employees.
- Emergency Reporting
List the emergencies to be reported to the emergency coordinator or area supervisor. These include fire, natural disaster, workplace violence, medical, off-site injury, hazardous material spill, etc.
- Evacuation Plans
Include the floor plans and exit routes for the employees to follow during emergencies.
- Employee Accountability Procedures after Evacuation
List the employees responsible for particular action after evacuation. Each of them will report to his/her supervisor to make an accurate headcount, who further reports to the emergency coordinator.
- Rescue or Medical Duties
Decide and include the way your employees will perform rescue or medical duties. For example, include contacts from local resources such as fire departments and hospitals, emergency services, and similar. And train the employees to give basic first aid until the help arrives.
- Critical Operations
List the employees delegated the responsibility of turning off the critical systems or utilities in case of emergencies. Make a similar table:
|
Name |
Equipment or Property to Secure |
Location of Equipment or Property |
Estimate time to complete the security process |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Training
Prepare a training plan for employees and managers for different tasks involved in the EAP.
- Emergency Phone Number List
Make a table of phone numbers you need to contact during emergencies, such as the fire department, police department, paramedic, security, building manager, etc.
Then, include the action plan for each emergency, including fire, natural disasters, workplace violence, hazardous material spills, etc.
EAP in Workplace FAQs
What size of solar generator is needed for an emergency in my workplace?
Investing in a solar generator is important in ensuring that your operations aren’t disrupted under any circumstances. To determine the needed size of a solar generator, consider the number of appliances you use and for how long.
For example, a Jackery Solar Generator 3000 Pro can charge a TV (300W), a computer (100W), and a refrigerator (1000W) for 1.8 hours.
Working Time = Capacity in Wh × 0.85 / Operating wattage of the appliances.
So, Working Time = 3024Wh × 0.85/1400W = 1.8H
Note: 0.85 is multiplied by the battery capacity to indicate the power loss while charging the devices.
What are the benefits of an emergency action plan?
Some of the key benefits of an emergency action plan include ensuring employee safety, reducing response time, fostering employee confidence, minimizing property damage, facilitating communication, and reducing financial loss.
Why is emergency planning important in the workplace?
Emergency planning in a workplace is important to ensure the good health and safety of the workers and minimize damage to the property.
What is the main purpose of an emergency plan?
The primary purpose of an emergency plan is for an employee and employer to adopt a proactive approach during emergencies at the workplace.
What are the 4 components of an emergency action plan?
The four components of an emergency action plan are mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery.
Emergency Action Plan at Workplace
We hope you have already gotten the answer to how an emergency action plan benefits your workplace. It fosters a safe and more prepared environment where every individual is aware of the emergency scenarios and involved in the planning process, which allows them to minimize injury, damage, and operational disruptions. Emergencies are often followed by power outages and blackouts, so investing in a Jackery Solar Generator would be a smart decision. These are efficient and reliable and power most of your appliances without disruption.


















































































































Leave a comment