Electricity is an important aspect of modern life. It plays a major role in everything from charging household appliances to powering industries. Understanding electricity terms like circuit breaker, kilowatt-hour (kWh), surge, etc., would help beginners make informed decisions about energy usage, safety, and efficiency.
Glossary List of Electricity Terms
There are hundreds of different electricity terms that help people understand how electricity is transferred and their electricity charges. The following glossary covers essential electricity terms to aid in understanding various aspects of the electrical system and related technologies.
A
Active Power : Active Power refers to the real power consumed by any given electric circuit, which distinguishes it from reactive power.
Admittance (Ω Ohms) : Admittance indicates the ease with which the current flows through a device or an electric circuit.
Alternator : Alternators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Alternating Current (A.C.) : An alternating current is an electric current that cyclically changes direction.
Aerial cable : These are insulated conductors installed on overhead structures.
Air Blast Breakers : These are commonly used in transmission-level applications, where high-voltage circuit breakers are used.
B
Battery : A battery is an energy storage device with one or more connected electric cells.
Battery Cell : Battery cells are electrochemical units that consist of positive and negative plates, a separator, and an electrolyte, which are used to store electrical energy.
Blackout : Blackout is the electricity term that denotes the complete loss of electric power from the power distributor.
Breakdown Voltage : Breakdown voltage is the voltage level at which a dielectric material experiences failure or complete breakdown.
C
Circuit : Circuit is an important term in electricity, providing a pathway through which electrical signal flows.
Circuit Breaker : A circuit breaker is a device designed to manually open or close an electrical circuit and automatically disconnect it if necessary.
Circuit Voltage : Circuit voltages are the highest effective potential difference between any two conductors in any given electrical circuit.
Current : Current is the flow of electric charge along a conductor.
Capacitor : A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electric energy.
Charge : Charge is an electric term that denotes the process of replenishing the active materials in a storage battery.
Circuit Switchers : These are the switching and protection devices used in different applications.
Current Flow : Current flow denotes the movement of electrons from atom to atom within a conductor.
Current Transformer : This is a type of transformer used to measure circuit current by transmitting a smaller, proportional current to any measuring device.
D
Deep Discharge (Battery) : Deep discharge happens when more than half of a battery's rated capacity is used up.
Design Load : Design load is the expected amount of usage that a device is designed to handle.
Digital : This electricity term is used in computer science to describe something created electronically.
E
Electric Current : Any movement of electric charges, typically carried by negatively charged particles through a conductor, is deemed an electric current.
Electric Field : An electric field is an area that surrounds a charged object where the force of electricity has an effect.
Electricity : Electricity is the flow of electrons from one atom to another within a conductor, generating an electric current.
F
Fault Current : Fault current is the current that occurs when a short-circuit condition arises.
Fault Indicators : These are the devices installed on a conductor to detect when the current exceeds a specified rating.
G
Gate : Gates are logical circuit devices that produce a binary output based on the input from other circuits.
Generator : Generators are machines that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Grid : The grid is the interconnected network of power stations and multiple transmission and distribution lines.
H
Hertz : It is a process of alternating between the negative and positive poles.
High Voltage System : It is an electric power system with a maximum root-mean-square A.C. voltage exceeding 72.5 kV.
I
Insulator : It is a material that prevents the flow of electric current through it.
Integrated Circuit (I.C.) : It is a miniaturized electronic circuit used to perform various electric functions.
K
Kilowatt (kW) : It is a unit of measurement for electric power.
Kilowatt Hour (kWh) : It is the amount of electric energy equivalent to one kilowatt of power consumed in one hour.
Kilowatt-hour Meter : It is a device that is used to measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by any system.
L
Light Emitting Diode (LED) : LEDs are semiconductors that emit light when a current flows through them.
Lightning : A powerful flash of light caused by an atmospheric electrical discharge between clouds and the earth's surface.
Limit Switch : These are protective devices that are commonly used in applications related to safety and control purposes.
Lines of Force : These invisible lines illustrate the characteristics of a magnetic flux around a magnet.
M
Magnet : It is an object that can attract iron or other magnets.
Meter : It is an instrument used to measure the quantity of something passing through it.
Microprocessors : These are integrated circuits that combine logic, amplification, and memory functions.
N
Neutral Ground Reactor : These are used to connect the neutral point of a three-phase electrical system to the ground.
Neutrons : These are uncharged elementary particles found in the nucleus of atoms.
Nickel Cadmium Battery : These are rechargeable batteries consisting of one or more cells with an alkaline electrolyte.
O
Off-Peak Hours : That period of time when the power supply demand on the power system is low.
Off-Load Tap Changer : This device is designed to adjust the transformer's voltage ratio when it is not supplying any load.
P
Parallel Circuit : This type of circuit configuration involves connecting the components in branches and providing multiple paths for the electrical components to flow.
Photovoltaic Cell : It comes under a photovoltaic module that converts light into electrical energy.
Protection Relay : It is designed to detect and respond to abnormal conditions in any electrical system.
R
Regulating Transformer : It is utilized to adjust the voltage of an output circuit.
Regulator : It regulates the current or voltage flow in a circuit to achieve a desired level.
Relay : This is an electrical switch operated by a small current to control a larger current flow.
Reluctance : Reluctance is a resistance offered by a magnetic circuit to the flow of magnetic lines of forces.
S
Semiconductor : They are used to make electronic components as they have properties between those of conductors and insulators.
Service Life (Battery) : The total duration for which a batter is useful.
Short Circuit : It is referred to as the fault that occurs when an underground conductor contacts another conductor.
Solar Energy : Solar energy is derived from the sun's heat or light. It is harnessed by solar panels and solar thermal systems.
T
Three-Phase : It is a power supply that utilizes at least three wires, where each wire carries a different voltage phase from a common generator.
Transformer : It is an electromagnetic device that is employed to alter the voltage in an A.C. electrical circuit.
U
Ultra High Voltage : These are the transmission systems where the A.C. voltage exceeds 800,000 volts.
Unbalanced Loads : These are unequal loading of the phases in a three-phase electrical system.
V
V : Typically, in electricity terms, V is the representation of Voltage.
Volt-Ampere : It is a unit of measurement for apparent power, which is calculated as the product of the root mean square voltage and current.
Voltage Class : These are the levels of electrical insulation strength on a device, which determines the maximum continuous voltage.
W
Watt : Watt is the effective power calculated by multiplying voltage, current, and power factor.
Watt-Hour : Watt-hours are used to measure energy usage in one hour.
Wattmeter : It is an instrument used to measure the electric power within a circuit.
Z
Zero Crossing : It is the point in a sinusoidal voltage waveform where it intersects the zero reference axis.
Basic Electricity Fundamental Laws
Since the electricity terms are extremely vast and complicated, it is always recommended to learn some of the basic fundamental laws of electricity. By understanding these laws, one can become more aware of different electricity terms.
Ohm's Law
Formula: V = I x R
Ohm's Law states that the Voltage (V) across a conductor is directly proportional to the Current (I) that flows through it, given the condition that the Resistance (R) remains constant.
Consider a circuit with a resistor of 15 Ω and a current of 2 A. By using Ohm's Law, the voltage drop across the resistor is V = I x R = 2A * 15 Ω = 30 V.
Watt's Law
Formula: P = V x I
Watt's Law relates Power (P) to Voltage (V) and Current (I). As per Watt's Law, the power consumed in an electric circuit is equal to the product of voltage and the current.
Consider a circuit that operates at 120 V and draws a current of 5 A. Then the power consumed by the circuit is P = V x I = 120 V x 5 A = 600 W
Joule's Law
Formula: Q = V x I x t
According to Joule's Law, the energy converted is proportional to the product of the voltage, current, and time.
Consider a resistor with a voltage of 10 V and a current of 2 A flowing through it for 10 s. Then, the energy dissipated as heat is Q = V x I x t = 10 V x 2 A x 10 s = 200 J.
Together, Ohm's Law, Watt's Law, and Joule's Law provide an extensive framework that is used by electrical engineers or students to analyze circuits and ensure efficient energy usage.
Jackery Portable Power Stations Explained
Jackery is a world-renowned brand in manufacturing and selling solar generators, solar panels, and battery backups. Jackery Explorer Portable Power Stations come with great battery capacities that can charge up to 99% of household appliances.
It is a battery-powered inverter generator that powers household appliances, like CPAP machines, coffee makers, and even appliances that are used in off-grid living adventures. The Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels absorb the sun's rays and convert them into D.C. electricity via monocrystalline silicon solar cells. The pure sine wave inverter later converts the stored electricity into A.C. current.
Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro Portable Power Station
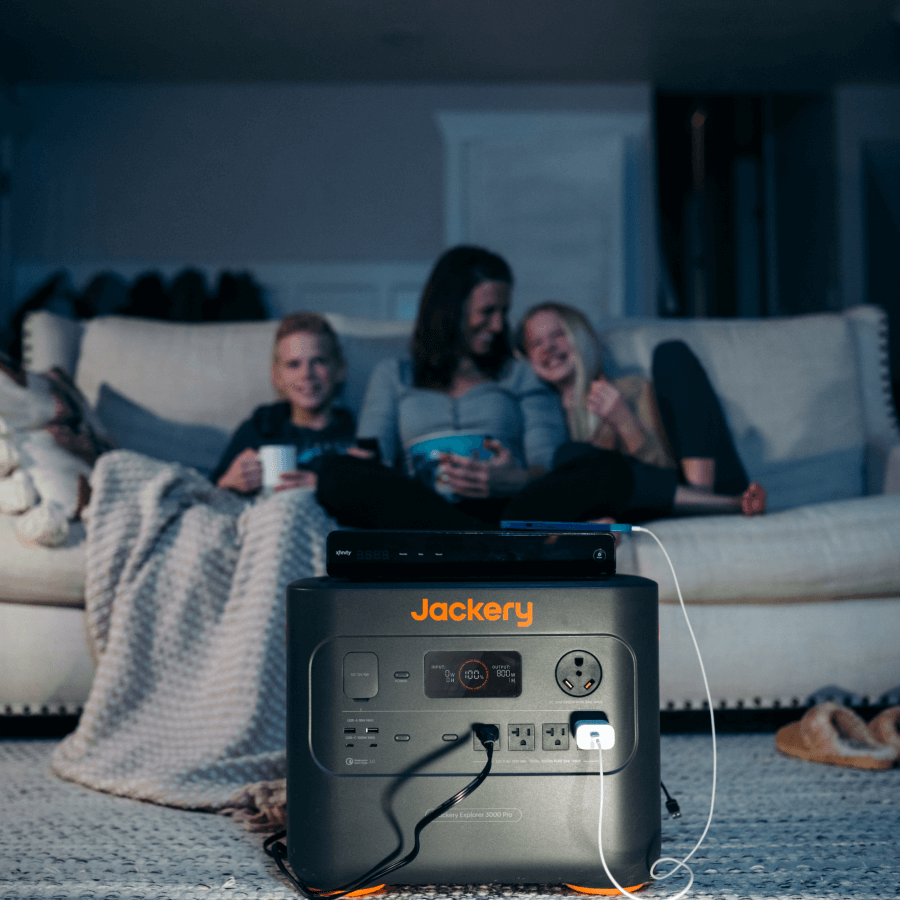
The Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro Portable Power Station can charge 99% of household appliances, such as televisions, coffee makers, and electric grillers. Its portable suitcase design makes it convenient for off-grid adventures.

|
|
Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro Portable Power Station |
|
Capacity |
3024 Wh |
|
Battery Cell |
NMC |
|
Cycle Life |
2000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar Recharging : 3.5 H (6*Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panels) Car Recharging : 35 H Wall Recharging : 2.4 H |
|
Output Ports |
AC Output (x1) : 120 V~ 60 Hz 25 A Max AC Output (x3) : 120 V~ 60 Hz 20 A Maximum USB-C Output (x2) : 100 W Maximum, 5 V⎓3 A, 9 V⎓3 A, 12 V⎓3 A, 15 V⎓3 A, 20 V⎓5 A |
|
Working Hours |
Vacuum Cleaner (1500 W) : 1.7 H Rice Cooker (1000 W) : 2.5 H Sump Pump (800 W) : 3.2 H Mixer Grinder (750 W) : 3.4 H Air Purifier (200 W) : 12.8 H |
|
Customer Review |
"I needed a reliable backup power solution that I could get in place quickly if a power outage occurred. The Jackery E3000 PRO is perfect." -- TMann Stuff |
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station has a LiFePO4 battery with a 10-year lifespan. It is ideal for off-grid living and powering household appliances during extended blackouts. This portable power station only needs 2 hours for a full solar charge, which is ideal for those constantly on the road.

|
|
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station |
|
Capacity |
2-24 kWh |
|
Battery Cell |
LiFePO4 |
|
Cycle Life |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar Recharging : 2 H (6*Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panels) Car Recharging : 25 H Wall Recharging : 2 H |
|
Output Ports |
AC Output (×4) : 120 V~ 60 Hz, 20 A Maximum AC Output (×1) : 120 V~ 60 Hz, 25 A Maximum USB-A Output (x2) : Quick Charge 3.0, 18 W Maximum USB-C Output (x2) : 100 W Maximum, (5 V, 9 V, 12 V, 15 V, 20 V up to 5 A) |
|
Working Hours |
Coffee Machine (1500 W) : 1.1 H Electric Kettle (1500 W) : 1.1 H Toaster (1100 W) : 1.5 H Air Purifier (200 W) : 8.6 H Standard Light Bulb (60 W) : 28.9 H |
|
Customer Review |
"I bought this specifically so I could plug in my freezer during a multi-day power outage. It appears to have enough power to run the freezer for two days." -- Anita Dyer. |
Jackery Explorer 2000 Pro Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 2000 Pro Portable Power Station is a lightweight power station, ideal for those who are looking for battery backup during campings or power outages. With a 2160 Wh NMC battery, it can charge up to 96% of household and off-grid appliances, like a television, griller, portable air conditioner, induction cooker, etc.

|
|
Jackery Explorer 2000 Pro Portable Power Station |
|
Capacity |
2160 Wh |
|
Battery Cell |
NMC |
|
Cycle Life |
1000 cycles to 80%+ capacity |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar Recharging : 2.5 H (6 * Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panels) Car Recharging : 24 H Wall Recharging : 2 H |
|
Output Ports |
USB-A Output (x2) : Quick Charge 3.0, 18 W Maximum AC Output (x3) : 120 V, 60 Hz, 2,200 W (4,400 W Surge Peak) USB-C Output (x2) : 100 W Maximum, (5 V, 9 V, 12 V, 15 V, 20 V up to 5 A) |
|
Working Hours |
Heater (1800 W) : 1 H Microwave (960 W) : 1.9 H Electric Grill (850 W) : 2.1 H Coffee Machine (1500 W) : 1.2 H Portable Air Conditioner (1150 W) : 1.5 H |
|
Customer Review |
"The Explorer 2000 was a piece of cake to set up and has been running as expected, with no glitches whatsoever, for almost 2 weeks, 24/7. My computer gear is happy, I'm happy, all is good." -- John Turner. |
Jackery Explorer 1500 Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 1500 Portable Power Station has a 1534 Wh battery capacity that can easily let you charge up to seven devices simultaneously. This portable power station uses solar energy directly from the sun instead of fossil fuel, which makes it a great addition for those who are looking for green energy sources.

|
|
Jackery Explorer 1500 Portable Power Station |
|
Capacity |
1534 Wh |
|
Battery Cell |
NMC |
|
Cycle Life |
800 Cycles to 80%+ Capacity |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar Recharging : 5 H (2 * Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panels) Car Recharging : 15.5 H Wall Recharging : 6 H |
|
Output Ports |
USB-A Output (x2) : Quick Charge 3.0x1, 18 W Max AC Output (x3) : 110 V, 60 Hz, 1,800 W (3,600 W Peak) USB-C Output (x1) : 60 W Max, (5 V, 9 V, 12 V, 15 V, 20 V up to 3 A) |
|
Working Hours |
Portable Air Conditioner (1150 W) : 1.1 H Microwave (960 W) : 1.3 H Electric Grill (850 W) : 1.5 H Refrigerator (800 W) : 1.6 H Mixer Grinder (750 W) : 1.7 H Laptop (70 W) : 18.6 H |
|
Customer Review |
"This is my 3rd Jackery battery! I have 3 different sizes." -- J.B. |
Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus Portable Power Station has a capacity of 1264 Wh and can charge 99% of appliances. With a compact design and lightweight, the Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus Portable Power Station is an ideal choice for camping, off-road travel, and home emergencies.

|
|
Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus Portable Power Station |
|
Capacity |
1.2 - 5 kWh |
|
Battery Cell |
LiFePO4 |
|
Cycle Life |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar Recharging : 3 H Car Recharging : 7 H Wall Recharging : 1.7 H |
|
Output Ports |
USB-A Output (x2) : 18 W Max, 5-5 V⎓3 A AC Output (x3) : 120 V, 60 Hz, 2,000 W (4,000 W Surge Peak) USB-C Output (x2) : 100 W Maximum, (5 V, 9 V, 12 V, 15 V, 20 V up to 5 A) |
|
Working Hours |
Microwave (960 W) : 1.1 H Electric Grill (850 W) : 1.2 H Mixer Grinder (750 W) : 1.4 H Mini Refrigerator (360 W) : 2.9 H Television (200 W) : 5.3 H |
|
Customer Review |
"Charged my Segway scooter, MacBook, and a couple of small gadgets. Jackery app enables you to control several functions of this power station." -- Chris. |
Electricity Terms FAQs
What are some words that relate to electricity?
Some of the common electricity terms are current, voltage, conductor, generator, solar energy, battery backup, and circuit breaker.
What is common in electrical terms?
Some of the commonalities in electrical terms are aspects of electrical circuits and components, like voltage, power, current, resistance, and conductance.
What are the 4 basic units of electricity?
The 4 basic units of electricity are Volt (V), Ampere (A), Ohm (Ω), and Watt (W).
What is the difference between energy and power?
The difference in energy and power can be explained via the following table:
|
Aspect |
Energy |
Power |
|
Definition |
Energy is a measure of the capacity to do any task or action. |
Power is the rate at which the said work is done. |
|
SI Unit |
Joule (J) |
Watt (W) |
|
Formula |
E = P x t |
P = E/t |
What is the flow of electricity called?
The flow of electricity or the movement of electric charges through a conductor is called current.
Final Thoughts
There are hundreds of electricity terms, and if one wants to understand how electricity is transferred from their service provider to their household, then getting acquainted with the basic electric terms is highly recommended. Jackery Explorer Portable Power Stations provides an optimal solution for those who want to reduce their electricity bill using solar energy.
















































































































Leave a comment