Are Batteries AC or DC? [Ultimate Guide]
Batteries are a major part of our modern lifestyle as we use them to power many of our appliances and devices, such as our smartphones. However, if you have ever wondered, are batteries AC or DC? As we all know, alternating and direct current are the two types of electricity; which category do you think a battery belongs to? This post will tell you everything about AC or DC batteries, also exploring their importance in power storage. We will also discuss how Jackery Portable Power Stations combine lithium-ion batteries with inverters and provide clean and cost-free AC and DC electricity.
|
Products |
Image |
Capacity |
Rated / Peak Power |
Battery |
Size |
|
Explorer 2000 Plus |
 |
2042 WH |
6000W |
LFP (Li-Fe PO4 Battery) |
Length= 14.7in Height= 14.1in Width= 18.6in |
|
Explorer 1000 Plus |
 |
1264 WH |
2000W |
LFP (Li-Fe PO4 Battery) |
Length= 14in Height= 11.4in Width= 10in |
Understand AC & DC
If you want to know what batteries are AC or DC, it is better to understand their difference. AC and DC are two main forms of electrical current utilized in many applications. They have different properties and current flow directions.
Alternating Current (AC):
AC reverses electron flow. The voltage and current levels change direction over time, usually in a sinusoidal waveform. AC circuits cycle between positive and negative voltage and current.
Applications of AC:
- AC is the most popular form of electrical power used in homes and businesses for lighting, appliances, and electronics. AC is used in these applications because it can readily be converted to other voltages for transmission and distribution.
- Electric Motors: From fans and blenders to enormous industrial equipment, AC powers electric motors.
- Generators: Because AC energy is readily produced and transferred over large distances, many power plants and generators create it.
- AC is utilized in speakers, amplifiers, radio broadcasts, and broadcasting.
Direct Current (DC):
DC is an electrical current in which electrons travel exclusively from positive to negative. DC circuit voltage and current never reverse.
Application of DC:
- Batteries power mobile phones, computers, and flashlights with DC power.
- Electronic Circuits: Computers, cellphones, and ICs need DC power.
- Electric Vehicles: DC power powers electric car motors and batteries.
- PV Cells: Solar panels create DC power that may be stored in batteries or converted to AC for homes and businesses.
- Rail Transportation: Many electric trains and trams utilize DC power.
AC and DC are separate electrical currents with different properties and uses. AC's alternating voltage and current make it ideal for power distribution and home uses. DC, utilized in batteries, electronics, and certain transportation systems, delivers a steady current flow in one direction. The application and energy transfer efficiency determines the decision between AC and DC.
Are Batteries AC or DC
For those of you wondering are batteries AC or DC? most batteries that you use and see in your daily life use direct current or DC. For batteries, this means that the electricity they store or create always moves in one direction, from the positive end to the negative terminal. One thing that makes DC power unique is that batteries create a steady flow of electrons that only goes in one way.
If we use AC to recharge batteries, then the charge will only flow into the battery for a short period, and after that, it will flow out of the battery. The reason behind this is explained by the name alternating current. So AC can't charge the battery, making it not a viable solution.
Due to this feature, batteries are perfect for running systems and devices that need a steady source of electricity flowing in one way, like electronics, lighting, cars, and many other uses. Power plants and the grid, on the other hand, usually send electricity in the form of alternating current (AC), which is better for long-distance transmission and distribution. However, many devices that get their power from the grid use rectifiers or power supplies to change the incoming AC power into DC power.
DC-Coupled VS AC-Coupled Batteries
If you are thinking, why are batteries AC or DC? It is time to figure out which one of these types is ideal for your use. Here is a detailed comparison of DC and AC batteries.
DC-Coupled Batteries:
DC-coupled batteries are directly linked to the DC side of solar PV systems or wind turbines. DC energy is stored and released, matching solar panel or power source output.
DC-Coupled Battery Pros:
- Higher Efficiency: DC-coupled systems convert less energy, making them more efficient. DC power from solar panels travels straight to the battery, reducing DC-to-AC and AC-to-DC losses.
- Because they are directly linked to the power source, DC-coupled batteries react faster to energy demand and grid circumstances.
- Compatible with Off-Grid Systems: In off-grid or isolated places with solar panels and wind turbines, DC-coupled batteries are employed.
DC-coupled battery cons:
- DC-coupled batteries are generally built for certain power sources and may not be as compatible with numerous inputs.
- DC-coupled system installation and configuration may need specialized equipment and knowledge.
Applications of DC-Coupled Battery:
- Off-Grid power systems
- Single-DC power source energy storage
The AC-Coupled Battery:
AC-coupled batteries are linked to the AC side of the electrical system downstream from inverters that transform DC electricity from solar panels or other sources into AC power. It only stores and releases AC electricity.
AC-Coupled Battery Pros:
- AC-coupled batteries may be incorporated into existing AC-based electrical systems, making them useful for retrofitting and extending solar PV installations.
- Flexibility: AC-coupled systems may use grid and renewable power.
- Easy Installation: AC-coupled batteries may be added to existing systems without any changes, making installation easier.
Cons of AC-Coupled Battery:
- AC-coupled systems may have decreased efficiency owing to AC-to-DC power conversions.
- Because they employ inverters, AC-coupled batteries may respond slower than DC-coupled batteries.
Applications of AC-Coupled Battery:
- Add energy storage to current solar PV systems
- Grid-connected homes and businesses seeking energy storage
|
Types of Batteries |
Pros |
Cons |
|
DC-Coupled Battery |
High Efficiency, Faster Response Time, Suitable for Off-Grid Systems |
Limited Compatibility, Complexity |
|
AC-Coupled Battery |
Compatibility, Flexibility, Easier Installation |
Slightly Lower Efficiency, Slower Response Time |
Which One to Use:
Here is a simple explanation as to why are batteries AC or DC. For storing energy, DC is more dependable than AC. Capacitors can store alternating current electricity, but their capacity is limited. DC electricity may be stored in significantly larger-capacity batteries. Furthermore, even when not connected to a circuit, capacitors lose their charge over time. Batteries, on the other hand, may hold their charge for an extended period of time.
How Does DC & AC Works?
Jackery Portable Power Stations deliver DC and AC power using lithium-ion batteries and inverters. Here is how they work:
DC Output:
Jackery power station stores energy in lithium-ion batteries. This stored energy is DC. DC connectors like 12V and USB enable you to draw power directly from the internal battery.
Mobile phones, LED lights, portable fans, and other low-voltage gadgets may be powered or charged in DC mode. The power station's internal battery supplies DC power, which is controlled to fit device needs.
AC Output:
The power station converts lithium-ion battery DC electricity into AC power using an inverter in AC mode. Inverters convert battery DC electricity into steady, sinusoidal AC waveforms.
Standard AC gadgets and appliances may be powered by Jackery power station AC outlets. TVs, computers, kitchen appliances, power tools, etc.
Jackery Portable Power Stations use lithium-ion batteries, DC power outputs, and inverters to provide transportable power. They offer DC and AC power for outdoor excursions, emergencies, and off-grid power. These power stations are convenient for storing and using electricity on the move or in remote areas.
Jackery Portable Power Station Explained
Jackery Portable Power Stations are small and dependable energy storage solutions for outdoor activities, emergency backup power, off-grid living, and other mobile needs. Jackery power stations are handy and eco-friendly devices to get power anywhere. Here is why you need a Jackery Portable Power Station.
Jackery power stations are lightweight and have ergonomic handles for portability. They're great for camping, RV lifestyle, tailgating, and other outdoor activities.
Clean and Quiet Energy: Jackery power plants employ lithium-ion batteries. They are noiseless and suited for restricted places and delicate surroundings.
Flexible Power Outputs: These power stations provide DC (for cellphones and portable fridges) and AC (for laptops, kitchen appliances, and power tools). Their USB ports charge tiny gadgets.
Rechargeable by Solar: Many Jackery types can be recharged by solar panels, which is beneficial in off-grid situations. During power outages, Jackery power plants provide backup power. They can power lights, freezers, and medical equipment.
Calculating Jackery Power Station Work Hours:
Consider the following parameters for calculating Jackery Explorer working hours:
Watt-hour battery capacity: Power stations' overall energy capacity is generally measured in watt-hours. A 1000Wh power station may potentially power a 100W device for 8.5 hours.
Efficiency Loss: Inverter and other components waste energy. Efficiency averages 85-90% across models.
Once you know the battery capacity, wattage of the device you want to run, and the efficiency loss percentage, you can calculate the working hours of your power station with this formula:
Working Hours = (Battery Capacity in WH) × 0.85 / (Device Power Consumption in W)
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus:

The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus is a portable, high-capacity power station that stores energy for several uses. It's ideal for outdoor enthusiasts, emergency backup power, and off-grid excursions because of its 2042Wh capacity, high power output, and charging compatibility. This tiny yet powerful machine lets you power important electronics and appliances on your travels while using clean, renewable energy.
Capacity: 2042Wh (watt-hours)
Rated Power: 2000W (watts), with a peak power of 4000W.
Battery: LFP (Li-Fe PO4 Battery) battery for reliable and efficient power storage.
Size: Length=14.7 in, Width=18.6 in, Height=14.1 in
Lifespan: The battery is designed to last through 4000 charge and discharge cycles.
Recharge Methods: You can recharge it through an AC wall outlet, 12V car outlet, or solar panels.
Features: The Explorer 2000 Plus offers multiple AC, DC, and USB outputs, an informative LCD display, and a user-friendly design. It's suitable for running a wide range of devices and appliances.
Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus:
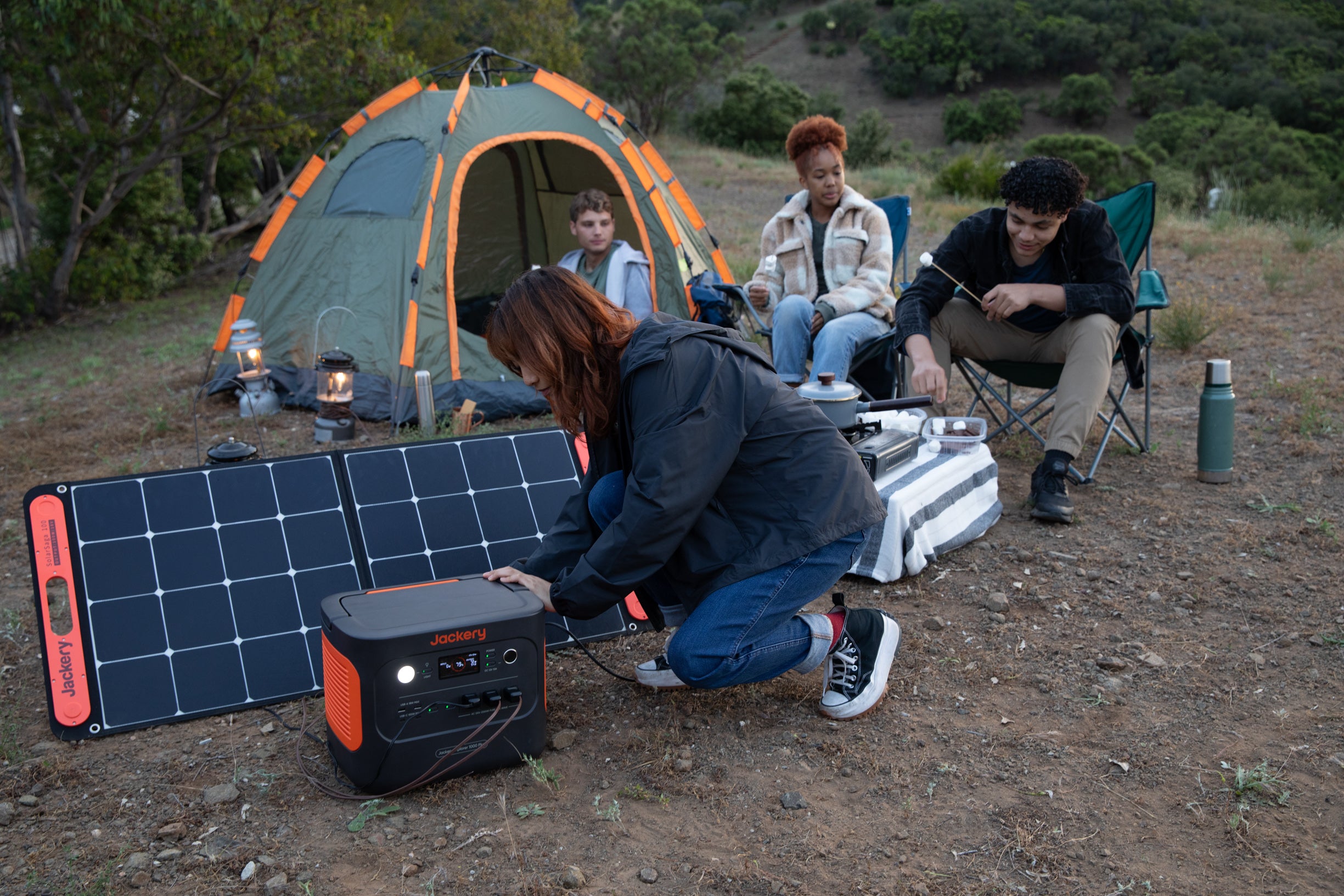

The small and efficient Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus portable power station provides consistent electricity for outdoor adventures and emergency backups. It powers your important electronics and appliances on the road with its 1264Wh capacity, powerful power output, and different charging choices.
Capacity: 1264Wh (watt-hours)
Rated Power: 2000W (watts)
Battery: Utilizes an LFP (Li-Fe PO4 Battery) battery.
Size: Height 11.4 in, Length 14 in, Width 10 in.
Lifespan: Its battery has a good lifespan and can endure 4000 charge and discharge cycles.
Charging Methods: You can recharge it via AC wall outlet, 12V car outlet, or solar panels (solar panels and accessories sold separately).
Features: The Explorer 1000 Plus provides a range of AC, DC, and USB outputs, making it versatile for various devices. It's known for its portability and ease of use.
Product Comparison Table:
|
Product |
Explorer 2000 Plus |
Explorer 1000 Plus |
|
Capacity |
2042 |
1264 |
|
Cycle Life |
4000 |
4000 |
|
Dimension |
Length=18.6 in, Width=14.1 in, Height=14.7 in |
Length=14 in, Width=10 in, Height=11.4 in |
|
Recharging Methods |
Solar panels, wall outlet, car, generator |
Solar panels, wall outlet, car, generator |
|
Output Ports |
AC outlet, USB-C, USB-A, carport, DC outlet |
AC outlet, USB-C, USB-A, carport, DC outlet |
Are Batteries AC or DC FAQs
- Are all batteries AC or DC? Are lithium batteries AC or DC?
DC is inherent in all batteries, even lithium-ion ones. Direct current, which flows from the battery's negative to the positive terminal, generates electricity. In contrast, AC (Alternating Current) reverses electron transport.
- Is a 12V battery AC or DC?
DC comes from 12V batteries. It creates and delivers constant direct current electricity. The 12V rating specifies DC power voltage.
- Why are batteries DC, not AC? (here mention Jackery Portable Power Station)
Jackery Portable Power Station batteries are DC sources because chemical reactions provide a unidirectional flow of electrons and a constant voltage and current. Jackery's lithium-ion batteries can convert from DC to AC, making them adaptable for outdoor and emergency power demands.
Final Thoughts
This answers the question: are batteries AC or DC? Batteries are DC (Direct Current) sources because chemical processes allow a continuous, unidirectional flow of electrons, resulting in steady voltage and current. DC is ideal for powering electronics that need a steady source. The Jackery Portable Power Station, with lithium-ion batteries and an inverter, illustrates this. Its flexibility to output DC and AC makes it useful for outdoor activities and emergency backup power.
Disclaimer:
The runtime mentioned for appliances powered by Jackery is for reference only. Actual runtime may vary under different conditions. Please refer to real-world performance for accurate results.








































































































Leave a comment