To build a secure emergency shelter, pick a location with two good trees or rocks to tie a long stick. Ensure the area is safe from falling trees or unstable rocks. Then, depending on the duration of the stay, build a lean-to or A-frame shelter. Clear the area of sticks and small stones, and use leaves, grasses, and boughs to build a bed.
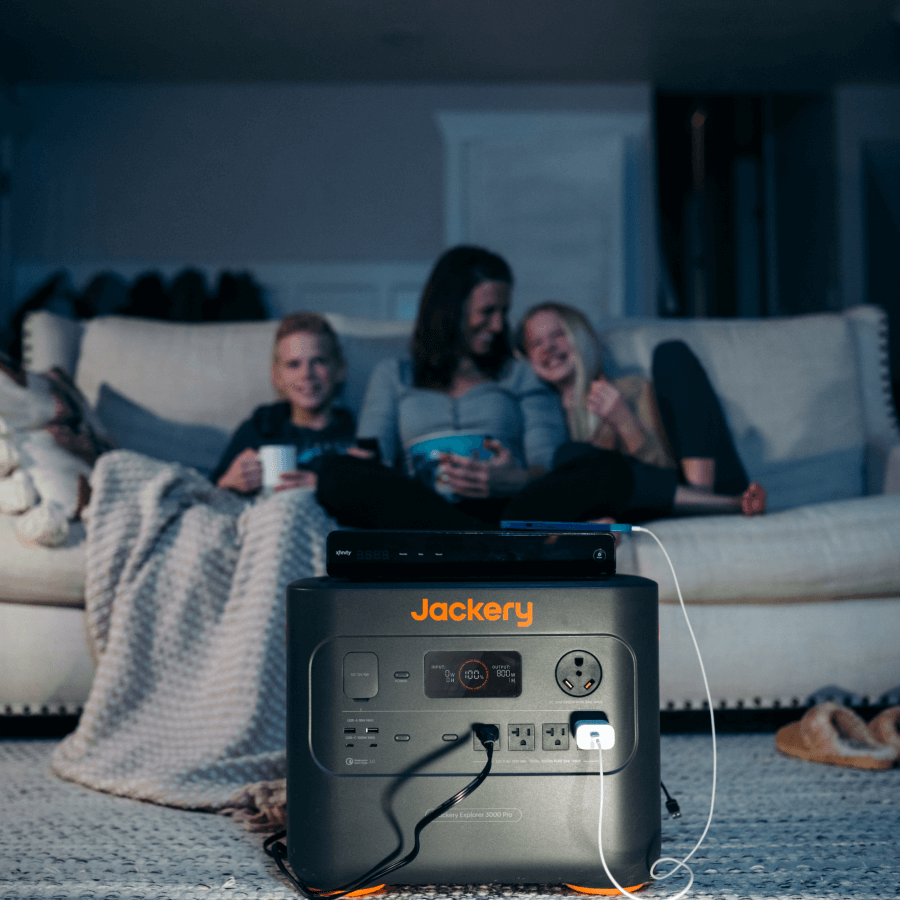
You’ll need devices to power the tools to build the shelter, cook food, and communicate. During emergencies, when the grid is down, solar generators can be a savior. Jackery Solar Generators are reliable solar-powered systems with various sizes and capacities. They can power essential appliances like electric saws, induction cooktops, heaters, and CPAP machines. These solar generators are easy to set up, maintain, and use sustainable energy as a power source.
Key Takeaways
- An emergency shelter is designed to keep people safe and secure in dire situations.
- Elevation, natural shelter, wildlife, and available resources are the factors to consider when building an emergency shelter.
- Some essential features in an emergency shelter are waterproofing, ventilation, fireproofing, security measures, and power options.
- To build an emergency shelter, you must select a suitable location, find suitable trees, build a bed, and keep the shelter warm.
What is an Emergency Shelter?
An emergency shelter is a temporary establishment for people who cannot stay at their home during natural disasters, war, or increasing crimes. There are special emergency shelters for women who seek special support services and homeless people. Not just a roof, these shelters offer support and resources to help people rebuild their lives for a better future. Here’s how people can benefit from an emergency shelter:
- Safety and Security: These are designed as safe places, protecting from potential dangers outside.
- Basic Needs: The occupants can easily access meals, showers, and hygiene products. This helps improve their health and well-being.
- Support Services: Besides essential services, emergency shelters provide access to support services such as mental health support and job placement.
- Community: Shelters provide a safe space where people with similar experiences can connect, receive support, and contribute to a collective environment.
How to Choose the Right Location for Your Emergency Shelter
Knowing where to build a shelter greatly increases your chances of survival. So, here are a few tips to consider when selecting the right location:
Elevation: Determining the optimal height of your shelter involves considering several key factors. For instance, avoid low areas, as they are mainly prone to floods, avalanches, mudslides, and falling rocks. In hilly terrain, the low-lying areas collect cold air during the night. Going up much higher creates challenges like strong winds and uneven terrain. So, the best bet would be to go typically about 3/4 of the way uphill.
Natural Shelter: Don’t overlook the natural shelters, as these can potentially be helpful. Sites like caves, large tree hollows, or boulders provide a temporary stay location. However, you might want to avoid these if you’re building an emergency shelter for women and children.
Wildlife: You must consider a few things when you’re planning to live in the woods. Stay near a food source while avoiding predators. With this in mind, keep the shelter away from a fruit tree as it attracts animals and insects.
Resources: This is one of the most important considerations when choosing the right location for an emergency shelter. Try to stay as close to an area with an ample supply of resources. This includes building materials and things like food, water, and others.
Essential Features of a Secure Emergency Shelter
Ventilation & air filtration, fireproofing, waterproofing, and power measures are some of the key features of a secure emergency shelter. Also, in emergency shelters for families, security measures like video surveillance systems are essential.
Ventilation and Filtration
An emergency shelter serves as a safety hut for people to survive a natural disaster, war, or other emergencies. You can store as much food and water as you want, but without fresh air, survival lasts only for days. It’s important that ventilators are installed, and air must pass through appropriate filters to trap the pollutants from outside.
FEMA recommends a class 2 filtration system with 99% filter efficiency when drawing outside air. Meanwhile, shelters must install HEPA filters with at least 99.97% efficiency to protect against highly toxic chemicals.
Waterproofing/ Drainage
Waterproofing the emergency shelter is especially important to ensure protection against heavy rain or floods. According to IFRC, shelters must fulfill the following criteria:
- Shelters are built with water-resistant materials or a protective coating to resist waterlogging and retain strength during heavy rain or flooding.
- They should have an adequate and well-maintained drainage system, which is also essential to remove the rainwater. Poorly managed drainage systems can erode the ground, leading to the instability of shelters.
- The doors and windows of the emergency shelter must be placed opposite each other for flash floods to flow out of the shelter. This prevents the walls from collapsing due to the high pressure of flood water.
- Rainwater gutters are also essential to run the water away from the roof and walls.
Fireproofing
Fire hazards are a common risk in many shelters, stemming from wildfires, lightning strikes, faulty electrical wiring, or overcrowding. To avoid that, check if the roof, walls, and floors of an emergency shelter use fire-resistant materials. Also, if there are necessary features like compartmentalization, proper ventilation, and designated fire exits to prevent the spread of fire.
Security Measures
Shelters and settlements, while providing safety, report cases of crimes. The risks are higher in emergency shelters for families. So, check for security measures like controlled access points, surveillance systems, and security personnel.
Power Options
In any emergency shelter, power is one of the most critical aspects. It’s essential for access to heating and cooling equipment, communication tools, medical equipment, water supply, and other critical devices.

Solar energy offers several advantages during emergencies when there are disruptions to the local power grid. It’s user-friendly, silent, and reliable. Jackery Solar Generators ticks all the boxes and runs essential appliances like CPAP, lights, video surveillance systems, and others for hours.
Emergency Shelter Supplies
If your stay in the emergency shelter is deemed to last a few days, here is the essential supplies list.

How to Build an Emergency Shelter at Home
Before you build a shelter, take time to evaluate the situation and your needs. If you’re looking for a long-term or short-term shelter, and whether your priority is warmth or protection. Answering these will help you decide if you’ll build an emergency shelter tent, an A-frame shelter, or an insulating debris shelter.
Step 1: Choose the Location
Choosing the right location is crucial as it directly impacts the safety and accessibility of occupants. To build your shelter, prefer a slightly elevated, flat area with rocks or trees. Also, ensure it’s away from hazards like falling branches, animal burrows, or unstable rocks.
Step 2: Choosing the Shelter Type
When building a temporary settlement to tackle emergencies, you cannot go on to spend hours sawing down poles or use dozens of cordage. This consumes time, risks injury, and uses up resources.

If you’re running out of time, build a lean-to shelter. It’s typically an emergency shelter for men, but if built right, it can also accommodate families.
- Find two trees at least seven feet apart and tie a long stick between them at waist height.
- The stick acts as your ridge pole. Then, lean smaller sticks at approximately 45-degree angles along the length of the pole.
- Cover the outside with pine needles, sticks, and others. Pile up the leaves until it’s about a foot thick.
If you have time, it’s recommended that you build an A-frame shelter. These guarantee warmth, which is crucial during colder weather. To build it, follow the steps in order:
- Locate a tree stump or a fallen tree, and prop one end of a long stick to it, with the other end into the ground.
- Use sticks along the ridge pole to build a triangle-like structure. Cover the outside with debris to insulate and keep you warm. Then, block the entrance with additional debris.
Step 3: Build a Bed
Beds are a useful addition to the shelters. They help keep you comfortable during uncertain situations. Clean the area of sticks and small rocks that could make sleeping uncomfortable. Or, use leaves, grasses, and boughs to make the softest bed. Use two logs side-by-side to build a frame, and fill the gaps with dead leaves, branches, or plants.
Step 4: Keep the Shelter Warm

Once you’ve built a shelter, a fire can keep you warm or cook your food. You can use an induction cooktop powered by Jackery Solar Generator. Not only food, but the solar generator can power CPAP machines or medical equipment running for a long time.
Jackery Solar Generators for Emergency Shelter
In emergencies, electricity serves as a crucial resource. It powers the essential equipment and systems that affect occupants' comfort, welfare, and safety. However, the power grid is down, a solar generator acts as an emergency power supply.
Jackery is a leading solar-powered product brand offering portable power stations, solar generators, and foldable solar panels. The Jackery Solar Generators combine Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels with Jackery Portable Power Stations to convert sunlight into usable electricity. They produce enough power to run most appliances during power outages and blackouts.
Jackery Solar Generator 5000 Plus
Jackery Solar Generator 5000 Plus is ideal for powering heavy-duty devices or the essentials for hours. It can power multiple devices simultaneously, making it suitable for extended outdoor stays. Whether they are critical equipment like CPAP machines, mobiles, and laptops or heavy-duty tools and appliances like saws, drills, or sanders, you can rely on the available power. Also, despite its large capacity, its pull rods and double wheels make it easy to move.
Appliance Running Hours:
- Electric Heater (1500W): 2.7H
- Electric Oven (2500W): 1.6H
- Cloth Dryer (2000W): 2.0H
- Induction Cooktop (1800W): 2.2H
- Refrigerator (900W): 4.5H

Customer Review:
“Awesome back-up unit. The wheels are pretty good. Three hours of home theater use (roughly 130 watts/hour) consumes about 10-15% of the inverter's charge.” - Telkwa.
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is another solar generator that can be useful during emergencies. It can power your TV to learn about the recent updates from officials, kitchen appliances to help cook food, and medical devices. The solar generator is expandable, so you can add multiple Jackery Battery Pack 2000 Plus if you need extra power to run your heavy-duty tools and appliances.
Appliance Running Hours:
- Refrigerator (900W): 1.8H
- Portable AC (500W): 3.3H
- Portable Heater (1000W): 1.6H
- Electric Saw (700W): 2.3H
- Mini-Induction Cooktop (600W): 2.7H

Customer Review:
“Charged it up to 100% really quickly and a couple of weeks later tested it by letting it run my full-size fridge. Ran it with no problem all day & half the night for about 16 hrs.” - Steve Dunn.
Costs of Building an Emergency Shelter
The cost of building an emergency shelter stays between $75 and $1000, depending on the type, materials used, location, and scale of construction. For example, a basic emergency shelter for youth won’t cost much, while it can be high for families. Irrespective of your needs, you will need items like building tools, insulation, first aid kit, etc.
|
Items |
Costs |
|
Tarp, Plastic Sheeting, or Tent |
$10-$150 |
|
Rope, paracord, or strong string |
$5-$20 |
|
Duct Tape |
$5-$15 |
|
Tools (multitool, knife, saw, or hatchet) |
$10-$100 |
|
Sleeping bag or natural insulation |
$20-$150 |
|
Rain Gear |
$5-$50 |
|
Wood and firestarter |
$1-$15 |
|
First Aid kit |
$10-$50 |
|
Compass or GPS device |
$10-$100 |
|
Flashlight or headlamp with extra batteries |
$10-$30 |
|
Total |
$75-$700 |
When building an emergency shelter, the items considered non-essential include a sleeping mat, pillow, camping chair, and more. Here’s a list and their estimated costs:
|
Items |
Cost |
|
Pillow or inflatable cushion |
$5-$30 |
|
Camping chair |
$20-$100 |
|
Sleeping mat |
$10-$50 |
|
Shovel or trowel |
$5-$30 |
|
Zip ties |
$2-$10 |
|
Mosquito Netting or Bug Spray |
$5-$20 |
|
Total |
$47-$240 |
Note: The estimated cost breakdown is based on general data, and the prices may vary depending on the brand, material, type, etc.
FAQs for Emergency Power Supply
What skills do you need to build an emergency shelter?
To build an emergency shelter, you must have skills such as identifying natural materials, cutting branches with a knife, tying knots securely, and utilizing natural resources like rock or tree roots.
What equipment is needed to build an emergency shelter?
You’ll typically need plastic sheeting or tarps, a knife or cutting tool, a strong rope, sturdy branches or sticks, and, depending on the environment, a hatchet or axe.
What are the most important factors to consider when choosing a location for a shelter on an island?
When choosing a location, it’s essential to consider its proximity to freshwater sources, elevation, access to food sources, and safety from wind and rain. Also, ensure it’s safe from wildlife and hazards like falling rocks.
What is the easiest shelter to build?
Lean-to is the easiest shelter to build. It only requires a few branches propped against a tree or rock, then covered with leaves or debris. It’s a basic shelter that protects from wind and rain.
What are the three types of shelters?
Shelters can be categorized as temporary, permanent, or survival shelters. You can select one depending on the emergency type, magnitude, and others. They are also categorized as no-barrier, low-barrier, or high-barrier.
Conclusion
An emergency shelter needs a power source to run all the essential and critical appliances and help occupants stay healthy and comfortable. A portable unit like Jackery Solar Generators can power refrigerators, overhead lights, medical equipment, and even heavy-duty appliances like ACs, electric saws, and more. Without power for days, you can cook your food and keep it fresh for days.
















































































































Leave a comment