Every year, the USA experiences hundreds of hailstorms, a weather phenomenon that occurs hand in hand with thunderstorms. While they manifest just about anywhere across the country, it’s the Great Plains that experience most of the hailstorms. With hail comes the anticipated impacts on public infrastructure, property, and agriculture.
Knowing the basics of hailstorms and their impacts allows us to devise adaptation measures for enhanced resilience. Here is a guide to help you understand the basics and take note of the best response strategies to counter hail damage, and how our battery power stations can protect you during a power outage.
Basics of Hail
Simply put, hail is a natural weather phenomenon in which solid ice forms during thunderstorms and rain down on the earth. Here is a closer breakdown of how hail forms and what makes it different from sleet.
▸ Formation Mechanism
Thunderstorms are usually the result of strong updrafts, warm air moving upward to the cooler atmosphere, along with downdrafts. These moving updrafts carry raindrops to the chilly atmosphere where they freeze over. As they collide with liquid water, more moisture freezes over the surface, causing the hail to grow in size.
▸ How It Falls
The hailstones will continue to grow in size at the chilling altitudes where temperatures drop to as low as -40°F. At some point, the weight of the hailstones is too much for the updraft to support them, or the updraft begins to weaken naturally. In either case, the hail storms will be pulled to earth, accelerated by the earth’s gravitational force pulling them down.
The smaller hailstones (less than an inch in diameter) typically fall at a speed of 9-25 mph, while the larger hailstones (1-1.75 inches) fall at a speed of 35-40 mph. The largest hailstones you might see, measuring anywhere from 2-4 inches, fall at speeds between 44-72 mph.[1] As the hail propels downward, the winds near the surface blow them at an angle or even completely sideways. This is why hail can always blow into your home, break your windows, damage your vehicles, and cause hail damage to public property.
▸ Appearance and Size
Hailstones come in layers of cloudy and clear ice and can look like pellets or balls. They are usually solid and hard to the touch, but some can be soft or spongy, depending on surface temperatures.
Furthermore, they vary considerably in size depending on how much moisture is frozen under their surface. They can vary anywhere from a quarter of an inch to larger than 4 inches in diameter. The largest hailstone to date measures around 9 inches in diameter, weighing 1 lb 15 oz, recovered in Vivian, South Dakota.[1]
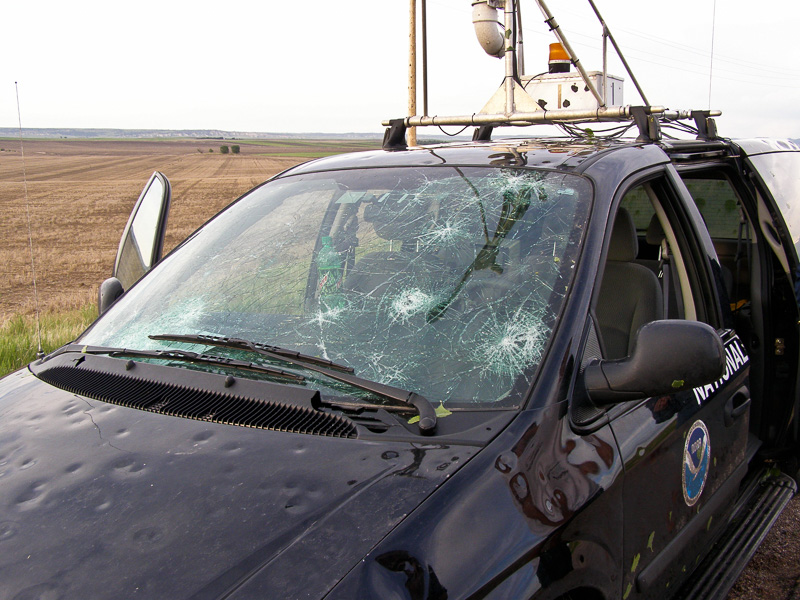

Source: NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory
Global Impacts of Hail Damage
Hailstorms prove to be highly costly not only for your property but also for your personal safety. Here are the many global impacts hailstorms pose:
▸ Potential Threats to Personal Safety
You might not experience it often, thanks to the safety of modern homes, but direct impact from hailstones can cause injury. According to the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, large enough hailstones have been known to cause concussions and even fatal head injuries.[2] They can cause injury to people and animals alike, which is why it is always recommended to seek shelter until the hailstorm subsides. If you are at home, it is best to close your shutters or blinds and stay away from the windows.
▸ Damage to Infrastructure
Hail can be heavily damaging to infrastructure. In fact, hail leads to the most storm damage costs across North America, leading to more than $10 billion in damages annually.[3] Hail damage can target parked vehicles, aircraft, glass-roofed structures, and public infrastructure, most important of which are your electrical systems.
The first thing you should check after a hailstorm is your power lines and electrical systems to weed out any hazards. It's natural for downed trees to impact power lines, often leading to fire risk. Moreover, if water penetrates into your electrical system, you will be at risk of short-circuiting.
▸ Direct Damage to Property
Hailstorms account for around 70% of all property damages during a storm.[3] Hail damage can impact your property's roof, dent your roof gutters, break your windows, damage your decks and porches, or at least chip down your property's paintwork. Sometimes, you may need to replace your roof entirely following a hailstorm, especially older roofs. The same applies to cracked glass doors or windows. If you have solar panels installed on the roof, they will likely be exposed to hail damage. You could counter this by investing in quality-tested glass-covered solar panels.
▸ Agricultural Losses due to Hail Damage
Large enough hailstones won't just damage your crops; they can lead to total losses and a drop in agricultural yield. They can bruise or puncture fruits, damage vegetables, break the branches off of trees, strip foliage, and damage leaves. It only takes one storm to lay damage to a year's worth of crop work.
How Can We Respond to Hail Damage?
Now that you know how damaging hailstorms can be to you and your property, how can you respond? Here are the strategic steps you can take to minimize the hail damage caused by hailstorms:
1. Prevention and Early Warning
The first step is to stay informed of weather updates. Keeping yourself up to date on weather patterns through your local weather forecasts means being one step ahead of a brewing hailstorm. If you know when it is about to hit, you can secure yourself and your property in time to reduce hail damage costs considerably. It is always better to be prepared than to be caught in the crosshairs of a thunderstorm.
2. Take Shelter in Time
If you have been notified of a potential hailstorm or are caught in one, the first logical step is to find shelter. You shouldn’t be indifferent to hail if it is small; these icy stones can always drop in large sizes. If you are not near your home, look for shelter nearby. If you are home, look out for your pets as well. Bring them indoors to keep them in a protected shelter. Remember to stay clear of windows and cover them with blinds or heavy drapes to keep hail out even if your window breaks. If possible, you should move to the basement or cellar, anywhere that is not directly below the roof until the storm passes.
If you are on the road, you should find a spot to safely pull over and protect yourself. Cover your head in case car windows shatter and injure you.
3. Place Things Properly
You can take several steps to minimize the hail damage to your property. Remove any weak branches or trees close to your home that may fly off with rising winds and land on your property. Move your patio furniture, garbage cans, potted plants, or other decor items into an indoor or sheltered place.
How to protect car from hail? Shift your vehicles to the garage. You can protect them further by placing hail guards on them. If you don’t have a garage, you can park them under the shelter of a tree to reduce the impact of hailstones.
4. Home Backup Power
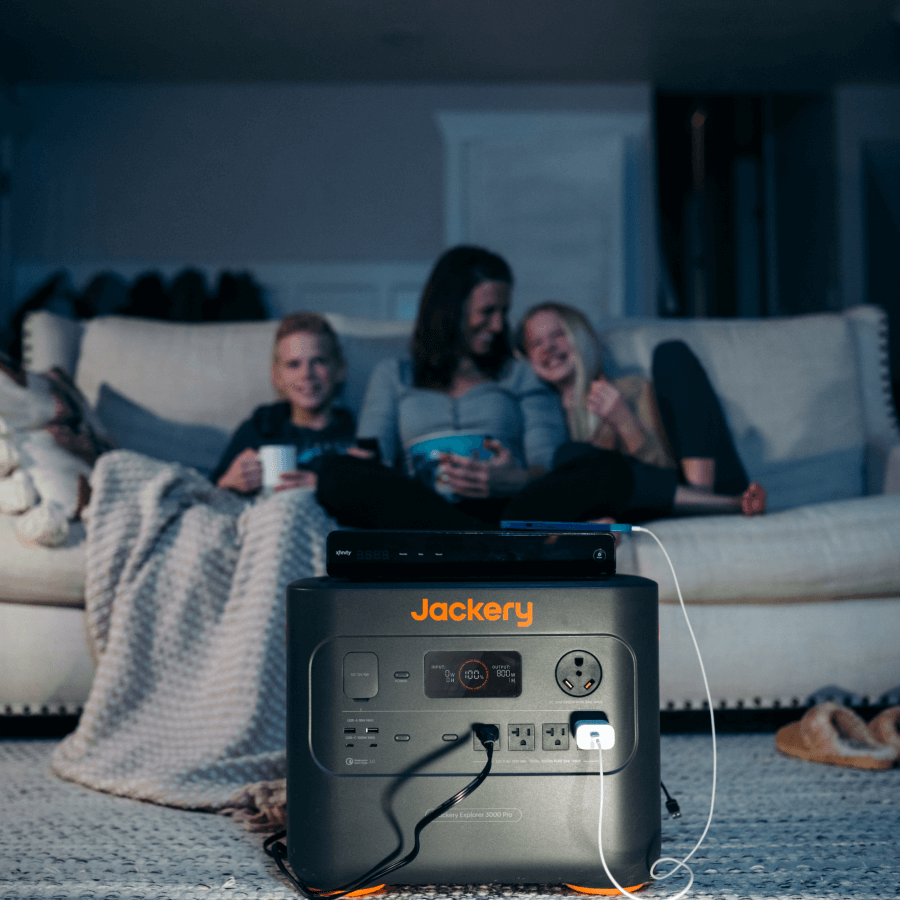
Hailstorms can cause significant hail damage to your property, notably your power lines and electrical systems. During a power storm, you will want to avoid using any electronics connected to the grid. Power surges during a storm can cause immediate and costly damages. Instead, you should have a backup power supply to rely on. A portable power station is a good choice, preferably one that can store charge for large periods and has enough battery capacity to power all your essentials.
5. Emergency Rescue and Clean-Up
Storms can be deadly and are notorious for the way they can disconnect you from nearby help. This is why it is always recommended that emergency resources be kept close to you. You will want a backup power supply to ensure you are not cut off from communications. The power supply will also power your clean-up tools after the storm. Stock up on an emergency first aid kit that you can use to cater to smaller cuts and bruising, but for more serious injuries, contact your nearest healthcare provider immediately.
6. Agriculture and Building Protection
For farmers looking to minimize hail damage to their crops, you can use hail nets to capture the hailstones, reducing their velocity. Now, about protecting your property, start with countering hail damage on the roof, which is the first layer of protection against hail. Impact-resistant roofing products can be used to strengthen your roof ahead of time. Place storm shutters close to your windows, skylights, and sliding doors. You may also get protective films installed to protect your glass windows.
Some property hazards don't manifest until after a storm clears away, so it is a good measure to check around your property for any damages, particularly to your roof and your power lines. If possible, you can capture photos of the hail damage early on to help with insurance claims.

Concerns About Purchasing A Portable Power Station
A portable power station is indispensable to power your essentials, such as flashlights, smartphones, radios, and other small devices during a hailstorm. But choosing the right one for your home is the catch.
You will have to assess several contributing factors: is the battery capacity sufficient for your home's needs? What charging options does it present? How many devices can it power at any time, and can its battery capacity be expanded further?
We recommend exploring our range of portable power stations to get an idea of what to expect from an ideal model:
Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 3000 Pro Portable Power Station is our first choice, primarily thanks to its stunning power capacity. With a capacity of up to 3024Wh, it can power up to 99% of appliances during a power outage; you won't have to worry about power outages in a hailstorm. Moreover, the portable solar panel has ultra-fast charging capabilities and can be recharged in multiple ways, such as via car battery, wall outlet, or solar panels. Despite its large lithium-ion battery, it comes in a neat, portable design that makes it ideal for use indoors and outdoors.
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station
The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station has an equally stunning power capacity of 2 kWh, but we like it for its expandability. It can be expanded by adding more battery packs to gain a capacity of 24 kWh! It has the same stellar ultra-fast charging capabilities (fully recharged with solar power in just 2 hours with six Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels). The best thing is that its battery uses LFP cells and is protected by Jackery’s Charge Shield technology to extend battery life.
Jackery Explorer 500 Portable Power Station
If you only want to power smaller devices such as flashlights or smartphones, this is the device for you. The Jackery Explorer 500 Portable Power Station comes with a battery capacity of 518 Wh and is fitted with the same industry-leading BMS technology as its other models. It has a portable ergonomic design, the same noiseless operation capabilities, and multiple input and output ports. Like the other power stations, you can recharge it using your car outlet, solar panels, or a wall outlet if that's convenient.
In short, when considering the purchase of a portable power station, be sure to select one that suits your home's needs in terms of capacity and functionality while also considering its reliability.
Final Thoughts
Homeowners must think of how hailstorms can cause damage to their property, downing power lines and blowing out power transformers. Power outages often come hand in hand with hail and thunderstorms. It is important to prioritize a backup power solution to rely on in the time of need. A small and portable power station can do wonders in providing you power when your house is cut off from the electrical supply. If you are unsure where to start, check out Jackery’s range of battery power station sets and portable solar panel solutions.
References
[1] NOAA National Severe Storms Laboratory-Hail. Available at:
https://www.nssl.noaa.gov/education/svrwx101/hail/ (Accessed: March 28, 2024)
[2] Hailstorms. Available at:
https://www.ifrc.org/our-work/disasters-climate-and-crises/what-disaster/hailstorms (Accessed: March 28, 2024)
[3] Most Storm Damage Caused by Hail. Available at:
https://eos.org/articles/hail-causes-the-most-storm-damage-costs-across-north-america (Accessed: March 28, 2024)

















































































































Leave a comment